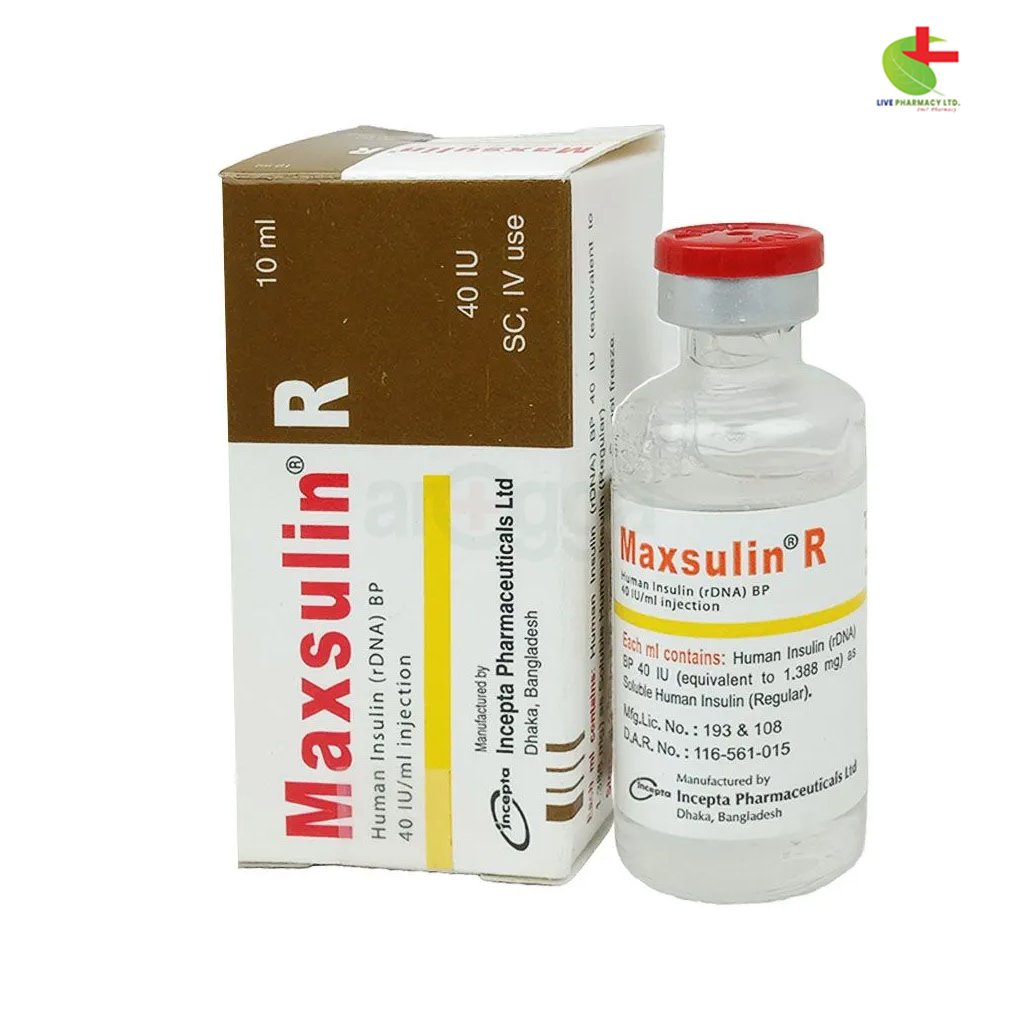
Maxsulin R 40IU Vial
195.00৳ Injection
- Maxsulin is an insulin product designed for the treatment of type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
- Manufactured by Incepta Pharmaceuticals Ltd., it offers effective glucose control and is available through Live Pharmacy.
- Maxsulin aids in the management of diabetes during various conditions, including gestational diabetes and hyperglycemic emergencies.
- Ensure proper administration and dosage adjustment under medical supervision for optimal results.
 Brand
Brand
|
Incepta Pharmaceuticals Ltd |
|---|---|
 Generics
Generics
|
Regular Insulin Human + Isophane Insulin Human |
 Type
Type
|
SC Injection |
Indications
- Management of Type 1 Diabetes: Essential for all patients diagnosed with type 1 diabetes.
- Support for Type 2 Diabetes: Effective for individuals with type 2 diabetes who struggle to maintain adequate control through diet and/or oral hypoglycemic medications.
- Initial Stabilization: Recommended for patients experiencing diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar non-ketotic syndrome, or during stressful periods like severe infections and major surgeries.
- Gestational Diabetes Treatment: Safe and effective for managing diabetes during pregnancy.
Consult a registered healthcare professional before using this medication.
Composition
- 30/70 Suspension: Each ml contains Insulin Human (rDNA) USP 100 IU (3.47 mg), comprised of 30% Regular Insulin Human and 70% Isophane Insulin Human.
- 50/50 Suspension: Each ml contains Insulin Human (rDNA) USP 100 IU (3.47 mg), consisting of 50% Regular Insulin Human and 50% Isophane Insulin Human.
Pharmacology
Insulin lowers blood glucose levels by enhancing glucose uptake through binding to receptors on muscle and fat cells while inhibiting glucose production in the liver. With a short half-life in the bloodstream, insulin does not significantly bind to plasma proteins.
Average Action Profile After Subcutaneous Injection:
- Onset of Action: Within 30 minutes
- Peak Plasma Levels: Reached within 1-3 hours
- Duration of Action: Approximately 18-24 hours
Dosage
Dosage is individualized and determined by a physician based on patient needs.
- Type 1 Diabetes Maintenance: Typical daily insulin requirements range from 0.5 to 1.0 IU/Kg, with pre-pubertal children needing 0.7 to 1.0 IU/Kg.
- Type 2 Diabetes Initial Dosage: Generally lower, around 0.3 to 0.6 IU/Kg per day.
- Post-Injection Timing: A meal or snack containing carbohydrates should follow an injection within 30 minutes.
Consult a registered healthcare professional before using this medication.
Administration
- Injection Sites: Primarily administered subcutaneously in the abdominal wall; the thigh, gluteal area, or deltoid region are also acceptable. Subcutaneous injections in the abdominal area facilitate faster absorption.
- Site Rotation: To prevent lipodystrophy, rotate injection sites within the same anatomical region.
Dosage Adjustment
- Illness, especially infections, can increase insulin needs.
- Renal or hepatic impairment may lower insulin requirements.
- Changes in physical activity or diet may necessitate dosage adjustments.
- When switching insulin preparations, close medical supervision is required.
Before Using Insulin 30/70
- Ensure you have the correct type of insulin.
- Inspect the cartridge, including the rubber plunger (stopper).
- Disinfect the rubber membrane with surgical spirit.
Do Not Use Insulin 30/70 If:
- The cartridge or device has been dropped or crushed, risking leakage or damage.
- It has been improperly stored or frozen.
- It is not uniformly white and cloudy after mixing.
Mixing the Insulin
- Before using the cartridge, gently move it between positions A and B (see instructions) to ensure the glass ball moves throughout the cartridge. Do this at least 20 times before the first use and 10 times before each injection, until the liquid appears uniformly white and cloudy.
- If the cartridge is in the delivery system, move the system gently between A and B for at least 10 times before each injection.
Injection Instructions
- Inject insulin subcutaneously, following the technique outlined in the delivery system manual.
- Keep the needle under the skin for at least 6 seconds to ensure complete delivery of the dose.
- Always remove the needle post-injection to prevent leakage and maintain insulin potency.
Consult a registered healthcare professional before using this medication.
Interaction
Other medications can impact insulin requirements.
- Reduce Requirements: Oral hypoglycemic agents, monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), non-selective beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, salicylates, and alcohol.
- Increase Requirements: Thiazides, glucocorticoids, thyroid hormones, beta-sympathomimetics, growth hormone, and Danazol.
Beta-blockers may mask hypoglycemia symptoms, while Octreotide/Lanreotide can either raise or lower insulin needs. Alcohol may enhance and prolong insulin’s hypoglycemic effects.
Contraindications
This insulin should not be administered to patients with hypoglycemia or hypersensitivity to human insulin or its excipients.
Side Effects
Adverse reactions to human insulin are typically dose-dependent and linked to its pharmacological effects. Hypoglycemia is the most common side effect, often resulting from an excessive insulin dose.
Possible symptoms include:
- Generalized skin rash, itching, and sweating.
- Gastrointestinal disturbances and angioneurotic edema.
- Breathing difficulties, palpitations, and hypotension.
Severe allergic reactions can be life-threatening. Temporary edema may occur upon starting insulin therapy.
Pregnancy & Lactation
Insulin therapy during pregnancy poses no risk to the fetus as it does not cross the placental barrier. Both hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia can lead to complications, making adequate control essential. Insulin needs typically decrease during the first trimester, rise in the second and third, and revert to pre-pregnancy levels postpartum. Nursing mothers can safely continue insulin treatment, although dosage adjustments may be necessary.
Precautions & Warnings
Improper dosing or discontinuing treatment in type 1 diabetes can lead to hyperglycemia and potentially fatal diabetic ketoacidosis. Hypoglycemia may occur with excessive insulin administration.
Patient Transfer Precautions: Switching to a different insulin type or brand should only be done under strict medical supervision. Changes in strength, brand, type, or method of manufacture can necessitate a dosage adjustment.
Before traveling across time zones, patients should consult a physician regarding insulin and meal timing adjustments.
Storage Conditions
Insulin should be stored between 2°C and 8°C (in a refrigerator). Do not use frozen insulin or any that appears clumped or frosted after mixing. Protect from light and excessive heat or sunlight. In-use cartridges may be kept at room temperature for up to 6 weeks below 25°C or 4 weeks below 30°C. Always mix thoroughly before use by rolling the cartridge gently between your hands.










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.