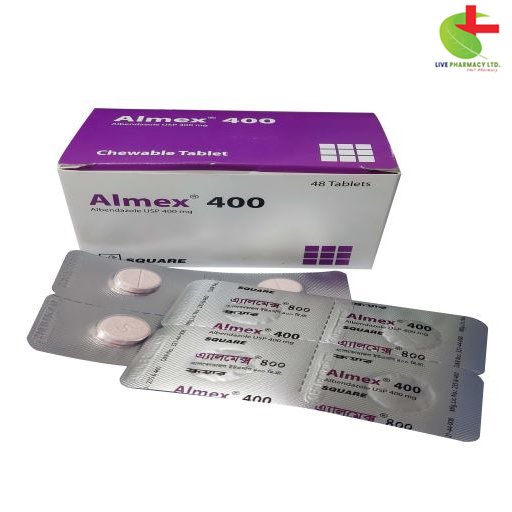
Almex 400
20.08৳ Strip
- Almex is a potent benzimidazole anthelmintic.
- It targets a wide spectrum of parasitic infections, including hookworm, roundworm, and tapeworm infestations.
- With its vermicidal, ovicidal, and larvicidal properties, Almex effectively eliminates various nematodes and cestodes.
- Its primary mode of action involves inhibiting tubulin polymerization, disrupting cytoplasmic microtubules and leading to parasite immobilization.
- Almex offers reliable treatment for intestinal nematode infections and hydatid disease, ensuring effective relief from parasitic burdens.
 Brand
Brand
|
Square Pharmaceuticals PLC |
|---|---|
 Generics
Generics
|
Albendazole |
Indications
Almex is recommended for the treatment of single and mixed infestations caused by various parasites including:
- Hookworm (Ancylostoma, Necator)
- Roundworm (Ascaris)
- Threadworm (Enterobius)
- Whipworm (Trichuris)
- Strongyloides
- Tapeworm
- Opisthorchi
- Hydatid
Description
Almex is classified as a benzimidazole anthelmintic, effective against a wide range of nematodes and some cestodes. It is primarily used to treat intestinal nematode infections and, in higher doses, for hydatid disease. Almex demonstrates vermicidal, ovicidal, and larvicidal properties. Its primary mode of action involves inhibiting tubulin polymerization, leading to the disruption of cytoplasmic microtubules.
Pharmacology
Albendazole, the active ingredient in Almex, is a broad-spectrum anthelmintic. It acts by exerting vermicidal, ovicidal, and larvicidal effects. The drug’s mechanism of action involves blocking glucose uptake in susceptible helminths, resulting in depletion of their energy reserves and subsequent immobilization. Albendazole is extensively metabolized, predominantly in the liver. Although poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, it undergoes rapid first-pass metabolism. The principal metabolite, albendazole sulphoxide, retains anthelmintic activity with a plasma half-life of approximately 8.5 hours and is excreted in urine along with other metabolites.
Dosage & Administration
For adults and children over 2 years old, a single dose of 400 mg (equivalent to 1 tablet or 10 ml suspension) is recommended for various parasitic infections. In cases of strongyloidiasis or taeniasis, the same dosage should be administered daily for three consecutive days. For children aged 1-2 years, a single dose of 200 mg (5 ml suspension) is recommended, while the use of Almex is not advised for children under 1 year old. In hydatid disease, the dosage varies based on patient weight, with treatment typically lasting for 28 days.
Interaction
No interactions, either pharmacodynamic or pharmacokinetic, involving Almex have been reported.
Contraindications
Albendazole is not recommended for use in neonates. Dosage adjustment may be necessary for children weighing less than 10 kg, but there is no general recommendation for reducing the dosage in children. Pregnant women should avoid Albendazole due to insufficient data on its safety during pregnancy and lactation.
Side Effects
Common side effects of Almex include gastrointestinal disturbances, headache, dizziness, and changes in liver enzymes. Rare side effects may include reversible alopecia, rash, fever, and blood disorders such as leucopenia and pancytopenia. Allergic shock may occur in cases of cyst leakage, while convulsions and meningism are possible in cerebral disease.
Pregnancy & Lactation
Albendazole is classified as Pregnancy Category C by the US FDA, indicating potential risks to the fetus. Therefore, its use during pregnancy and lactation should be avoided unless the benefits outweigh the risks.
Precautions & Warnings
Prior to treatment initiation and during each cycle, blood counts and liver function tests should be performed. Almex should be used cautiously during breastfeeding, and pregnancy should be excluded before starting treatment for hydatid disease. Constant medical supervision is necessary when using Almex for echinococcosis, with regular monitoring of serum-transaminase concentrations, leucocyte, and platelet counts.
Therapeutic Class
Almex belongs to the therapeutic class of anthelmintics.
Storage Conditions
Store Almex in a dry place, away from light and heat, and ensure it is kept out of reach of children.










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.