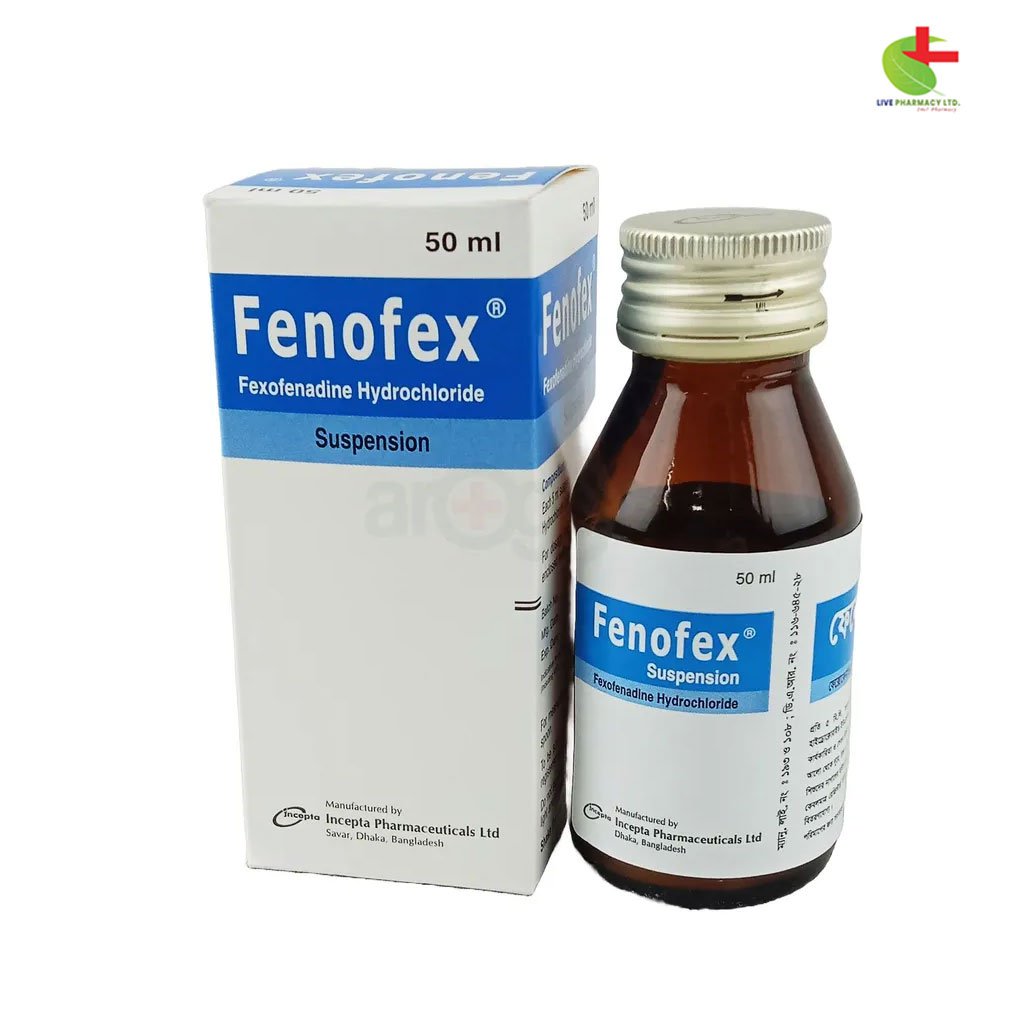
Fenofex Oral Suspension
60.00৳ Bottle (60gm)
- Indications: Fenofex is indicated for the relief of symptoms associated with seasonal and perennial allergic rhinitis in adults and children aged 12 and older.
- Pharmacology: It acts as an inverse agonist at H1 histamine receptors, preventing allergic symptoms without significant CNS effects.
- Dosage: Available in tablet and suspension forms, with specific dosages for different age groups and renal function considerations.
- Side Effects: Common side effects include headache, dizziness, and fatigue; hypersensitivity reactions are also possible.
- Precautions: Use with caution in elderly and patients with renal impairment; not recommended during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
 Brand
Brand
|
Incepta Pharmaceuticals Ltd |
|---|---|
 Generics
Generics
|
Fexofenadine Hydrochloride |
 Type
Type
|
Oral Suspension |
Indications
Allergic Rhinitis: Fenofex is prescribed to alleviate symptoms associated with both seasonal and perennial allergic rhinitis in adults and children aged 12 years and older. It effectively treats symptoms such as sneezing, runny nose (rhinorrhea), watery eyes (lacrimation), and itching of the nose, throat, and palate.
Important: Always follow the advice of a registered healthcare professional when taking any medication.
Pharmacology
The H1 histamine receptor plays a key role in mediating hypersensitivity and allergic reactions. When exposed to allergens, mast cells and basophils degranulate, releasing histamine and other inflammatory mediators. Histamine then binds to H1 receptors, triggering the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines like interleukins, resulting in various allergic symptoms such as itching, runny nose, and watery eyes.
Fexofenadine is classified as an “inverse agonist” of the H1 receptor, as it binds to and stabilizes the receptor in its inactive form. This action prevents receptor activation and its subsequent effects. Fexofenadine exhibits strong selectivity for H1 receptors and does not demonstrate any antidopaminergic, antiserotonergic, anticholinergic, sedative, or adrenergic blocking activity. Furthermore, it does not cross the blood-brain barrier, making significant central nervous system effects unlikely.
Dosage & Administration
For Allergic Rhinitis:
- Adults and Children (12 years and older):
- Tablet: 60 mg twice daily or 120 mg once daily or 180 mg once daily
- For renal impairment: 60 mg once daily
- Children (6 to 11 years):
- Tablet: 30 mg twice daily or 60 mg once daily
- For renal impairment: 30 mg once daily
- Children (2 to 11 years):
- Suspension: 30 mg (5 ml) twice daily
- For renal impairment: 30 mg (5 ml) once daily
For Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria:
- Adults and Children (12 years and older):
- Tablet: 60 mg twice daily or 120 mg once daily or 180 mg once daily
- For renal impairment: 60 mg once daily
- Children (6 to 11 years):
- Tablet: 30 mg twice daily or 60 mg once daily
- For renal impairment: 30 mg once daily
- Children (6 months to less than 2 years):
- Suspension: 15 mg (2.5 ml) twice daily
- For renal impairment: 15 mg (2.5 ml) once daily
- Children (2 to 11 years):
- Suspension: 30 mg (5 ml) twice daily
- For renal impairment: 30 mg (5 ml) once daily
Important: Always follow the advice of a registered healthcare professional when taking any medication.
Interaction
Fenofex is not metabolized in the liver and thus does not interact with other medications through hepatic mechanisms. Co-administration with erythromycin or ketoconazole may increase plasma levels of fexofenadine by 2-3 times without affecting the QT interval or increasing adverse reactions. There is no interaction noted between fexofenadine and omeprazole. However, taking antacids containing aluminum and magnesium hydroxide 15 minutes before fexofenadine may reduce its bioavailability. It’s recommended to allow a 2-hour gap between these medications.
Contraindications
Fenofex is contraindicated for individuals with known hypersensitivity to fexofenadine hydrochloride or any of its components.
Side Effects
The following frequency ratings apply: Very common (≥1/10); Common (≥1/100 and <1/10); Uncommon (≥1/1,000 and <1/100); Rare (≥1/10,000 and <1/1,000); Very rare (<1/10,000; frequency cannot be estimated from available data). In clinical trials, the most commonly reported side effects in adults included:
- Nervous System Disorders: Common occurrences of headaches, drowsiness, and dizziness.
- Gastrointestinal Disorders: Common occurrences of nausea.
- General Disorders: Uncommon occurrences of fatigue.
Post-marketing surveillance reports additional side effects, though their frequency is not well-established. These may include hypersensitivity reactions (such as angioedema and chest tightness), psychiatric issues (including insomnia and nervousness), cardiac disorders (like tachycardia), gastrointestinal issues (such as diarrhea), and skin reactions (like rash or urticaria).
Pregnancy & Lactation
There is limited data on the use of fexofenadine hydrochloride in pregnant women. Animal studies show no direct or indirect harmful effects concerning pregnancy, fetal development, or postnatal growth. It is recommended to avoid using fexofenadine during pregnancy unless absolutely necessary.
Fexofenadine has been shown to pass into human breast milk when nursing mothers have taken terfenadine. Therefore, it is not recommended for breastfeeding mothers. There is insufficient data regarding the effects of fexofenadine on fertility in humans; however, studies in mice indicate no adverse effects on fertility.
Precautions & Warnings
Due to limited data, caution is advised when administering Fenofex to elderly patients and those with renal or hepatic impairment. Individuals with a history of cardiovascular disease should be warned that antihistamines may cause tachycardia and palpitations.
Effects on Ability to Drive and Use Machinery: Based on its pharmacodynamic profile, Fenofex is unlikely to affect the ability to drive or operate machinery. Objective tests indicate no significant impact on central nervous system function, but individuals should assess their own response to the medication before engaging in potentially hazardous activities.
Use in Special Populations
Renal and Hepatic Impairment: The pharmacokinetics of fexofenadine are altered in individuals with renal impairment. A starting dose of 60 mg once daily is recommended for those with decreased renal function. Moderate to severe hepatic disease does not significantly affect fexofenadine pharmacokinetics.
Elderly Patients: Adverse events in elderly patients are comparable to those in younger populations, but increased bioavailability of fexofenadine has been noted in individuals over 65 years of age.
Overdose Effects
Overdose may lead to symptoms such as dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue, and dry mouth. Healthy subjects have tolerated single doses up to 800 mg and doses up to 690 mg twice daily for one month without significant adverse reactions compared to placebo. The maximum tolerated dose for Fenofex has not been established. Standard measures should be implemented to remove any unabsorbed medication, and symptomatic and supportive treatment is recommended. Hemodialysis does not effectively eliminate fexofenadine from the bloodstream.
Therapeutic Class
Non-sedating antihistamines
Storage Conditions
Store in a cool, dry place, away from light and heat. Keep out of reach of children.










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.