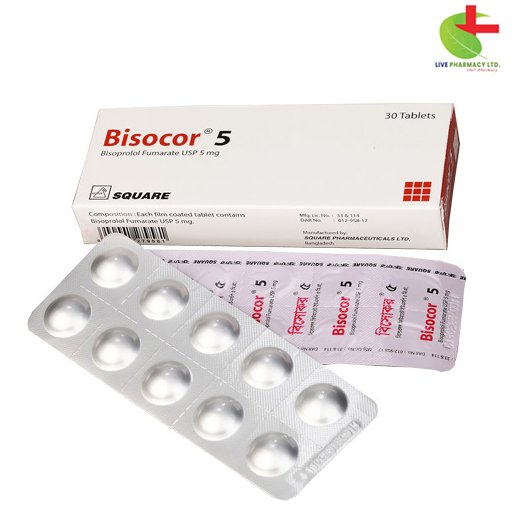
Bisocor 5
115.00৳ Strip
- Bisocor: Trusted medication for hypertension, angina, and heart failure.
- Superior ß1 blocking properties reduce heart rate and arterial hypertension.
- Once-daily dosing ensures therapeutic reliability.
- Minimal side effects for safe and effective management of cardiovascular conditions.
 Brand
Brand
|
Square Pharmaceuticals PLC |
|---|---|
 Generics
Generics
|
Bisoprolol Hemifumarate |
Indications
Bisocor serves as a treatment for:
- High blood pressure (Hypertension)
- Chest pain (Angina)
- Moderate to severe heart failure
It’s important to note that Bisocor is not advisable for immediate treatment during hypertensive crises.
Pharmacology
Bisoprolol Hemifumarate stands out as the most selective ß1 blocker, demonstrating a superior affinity for the ß1 receptor compared to other available beta-blockers. By selectively blocking ß1 adrenergic receptors in the heart and vascular smooth muscle, it effectively reduces heart rate and cardiac output, consequently lowering arterial hypertension. Unlike non-ß1 selective ß1-blockers, Bisoprolol doesn’t impact lipid metabolism, including cardioprotective HDL-cholesterol, during long-term therapy.
The pharmacokinetic properties of Bisoprolol support once-daily dosing, ensuring minimal variability in plasma concentration profiles and enhancing therapeutic reliability.
Dosage & Administration
For adults treating mild to moderate hypertension, the initial dose typically starts at 5 mg once daily, either alone or with a diuretic. Adjustments may be made based on individual patient needs, with a maximum dosage of 20 mg once daily. Dosage adjustments should occur at intervals of two weeks. It’s important to note that exceeding 20 mg daily yields marginal benefits.
Safety and efficacy for children have not been established, while caution is advised for patients with renal or hepatic impairment.
Interactions
Combining Bisocor with other ß-blocking agents is not recommended. Additionally, patients taking catecholamine-depleting drugs should be closely monitored due to potential excessive reduction in sympathetic activity.
Contraindications
Bisocor is contraindicated in patients with conditions such as cardiogenic shock, overt heart failure, second or third-degree A-V block, right ventricular failure secondary to pulmonary hypertension, and sinus bradycardia.
Side Effects
Individuals may experience varying side effects, including fatigue, dizziness, headache, gastrointestinal disturbances, cold extremities, muscle weakness or cramps, and breathing difficulties.
Pregnancy & Lactation
While studies have shown teratogenic effects in animals, data on pregnant women are lacking. Bisocor use during pregnancy should be carefully weighed against potential risks. Regarding lactation, caution is advised, as the drug’s excretion in human milk is not established.
Precautions & Warnings
Special caution should be exercised when adjusting Bisocor dosage in patients with impaired renal or hepatic function. Patients with a history of severe anaphylactic reactions may exhibit heightened sensitivity to allergens while on beta-blockers.
Storage Conditions
Bisocor should be stored in a dry place away from light and heat, and kept out of reach of children.
Chemical Structure
Molecular Formula: C18H31NO4
Common Questions
- Bisocor is a beta-blocker medication used to lower blood pressure, reduce heart workload, and prevent chest pain.
- It should be taken orally once daily, with or without food, preferably at the same time each day.
- Side effects may include dizziness, fatigue, headache, slow heart rate, difficulty breathing, and cold extremities.
- Bisocor is generally safe, but individuals with certain health conditions should consult a doctor before use.
- It’s recommended to take Bisocor after food and store it in a cool, dry place, away from children and pets.
Quick Tips
- Beware of potential dizziness; rise slowly from sitting or lying positions.
- Bisocor may mask symptoms of low blood sugar in diabetic individuals; monitor blood sugar levels regularly.
- Avoid sudden cessation of Bisocor, as it may spike blood pressure, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke.










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.