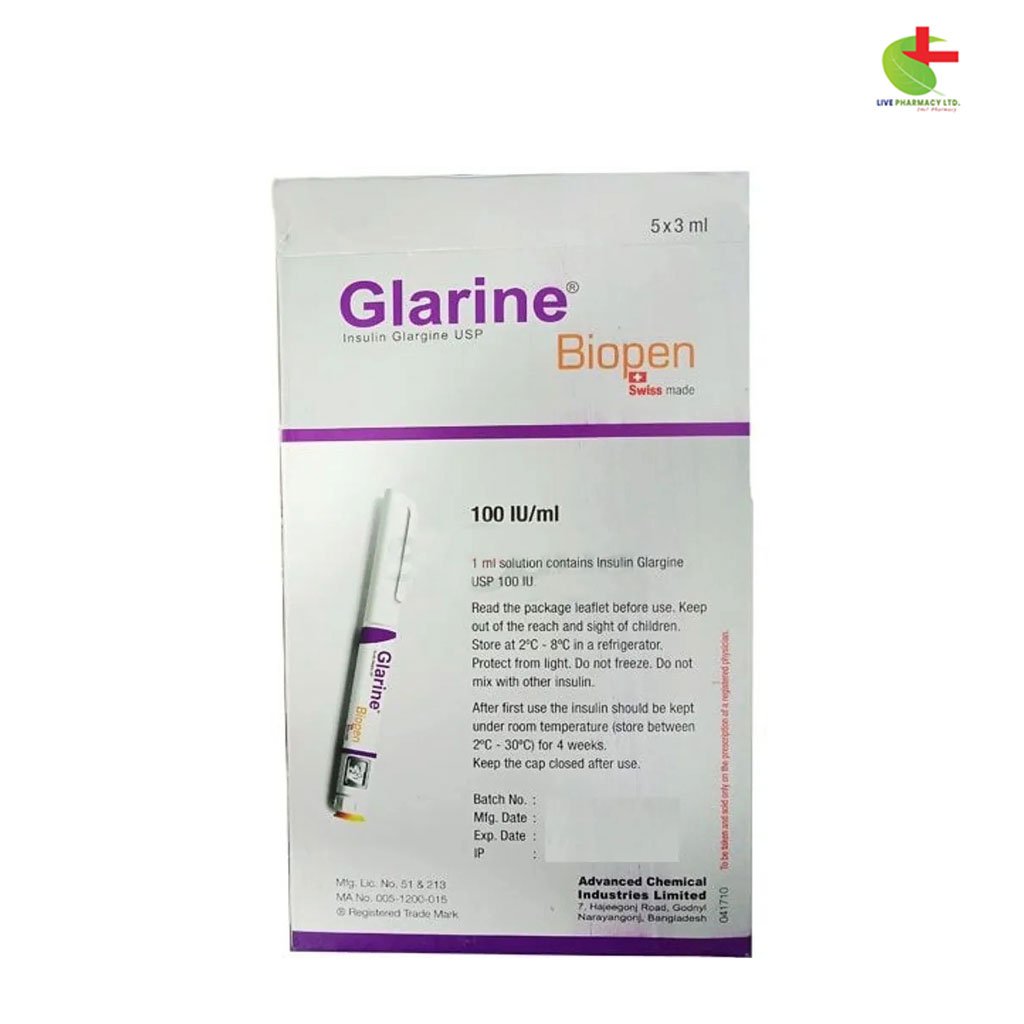
Glarine Biopen
950.00৳ Biopen(3ml)
- Glarine is a long-acting insulin used to control blood sugar levels in adults and children with type 1 diabetes and adults with type 2 diabetes.
- It is administered once daily via subcutaneous injection, with effects lasting up to 24 hours.
- Glarine helps regulate glucose metabolism by enhancing glucose uptake and inhibiting glucose production.
- Dosage is individualized based on clinical response and blood glucose monitoring.
 Brand
Brand
|
ACI Limited |
|---|---|
 Generics
Generics
|
Insulin Glargine |
 Type
Type
|
SC Injection |
Indications
Glarine is prescribed to aid in the regulation of blood sugar levels in both adults and children with type 1 diabetes mellitus and adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Please follow the guidance of a registered healthcare professional when using this medication.
Pharmacology
Glarine is a sterile insulin glargine solution designed for subcutaneous injection. It is a long-acting insulin analogue, with effects lasting up to 24 hours, created using recombinant DNA technology. This medication primarily regulates glucose metabolism by enhancing glucose uptake in muscles and fat, while also inhibiting glucose production in the liver. Insulin and its analogues lower blood glucose by promoting peripheral glucose absorption and suppressing lipolysis and proteolysis, fostering protein synthesis.
Dosage
Insulin Glargine has a consistent glucose-lowering action over 24 hours, allowing for once-daily dosing. The potency of insulin glargine is similar to that of human insulin.
- Administration: Insulin Glargine is recommended for subcutaneous injection once daily, at any time of day. Once you start using it, maintain consistency by administering the dose at the same time each day.
- Adjusting the Dose: The dosage should be tailored to the individual patient, based on their clinical response. Regular blood glucose monitoring is essential for all patients with diabetes.
- For Type 1 Diabetes: Insulin Glargine should be used in combination with short-acting insulin.
- For Type 2 Diabetes: The initial dose is 10 units or 0.2 units per kg, administered once daily, with adjustments made as necessary.
- Transitioning from Other Insulin Regimens: When switching from another long-acting insulin to Glarine, the initial dose should match the dose of the previous insulin. If switching from twice-daily NPH insulin, the initial Glarine dose should be 80% of the previous dose.
Please follow the advice of a registered healthcare professional when using this medication.
Administration Instructions
- Cartridge Use: Insert the cartridge into the pen and attach the needle. Gently shake the pen for 8-10 times to ensure uniform mixing. Set the dose using the dosage button. Discharge any air bubbles and inject as prescribed.
- Vial Use: Clean your hands and shake the vial gently to mix. After removing the protective cap, wipe the stopper with an alcohol swab. Draw air into the syringe equivalent to the insulin needed, then puncture the vial and inject the air. Withdraw the required dose, checking for air bubbles and removing them as necessary.
Injection Site: Preferred areas include the upper arm, thigh, abdomen, and buttocks. Rotate injection sites to avoid tissue damage, keeping at least 1 cm distance between injection spots.
Injection Technique: Clean the skin with an alcohol swab, and inject the insulin at a 45° angle. After injection, apply gentle pressure on the site but avoid rubbing.
Please follow the advice of a registered healthcare professional when using this medication.
Drug Interactions
Several drugs can influence glucose metabolism, requiring adjustments to Glarine’s dosage.
- Drugs that reduce Glarine’s effects: Oral anti-diabetic medications, ACE inhibitors, fluoxetine, certain antibiotics, and more.
- Drugs that may increase Glarine’s effects: Thiazides, glucocorticoids, thyroid hormones, growth hormone, and others.
Contraindications
Glarine should not be used by individuals with a known allergy to insulin glargine or any of its components.
Side Effects
Common side effects include hypoglycemia, allergic reactions, injection site reactions, lipodystrophy, itching, and rashes.
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy Category C. Glarine should only be used during pregnancy if the benefits outweigh the risks. It is unknown whether insulin glargine is excreted in human milk, so caution is advised for lactating women. Insulin doses may need to be adjusted during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Precautions & Warnings
- Monitoring: Regular blood glucose monitoring is vital for patients using Glarine.
- Administration Restrictions: Glarine should not be diluted or mixed with other insulin or solutions, and it must not be injected intravenously or via an insulin pump due to risk of severe hypoglycemia.
- Renal or Hepatic Impairment: Dose adjustments may be necessary for patients with kidney or liver issues.
Overdose
Overdosing on Glarine may lead to hypoglycemia. Mild episodes can typically be corrected with oral glucose. Severe hypoglycemia may require intravenous glucose or glucagon injections. Adjustments to dosage, meals, and exercise may be needed.
Therapeutic Class
Long-acting insulin.
Storage Conditions
Store between 2°C and 8°C. Do not freeze. Protect from light.










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.