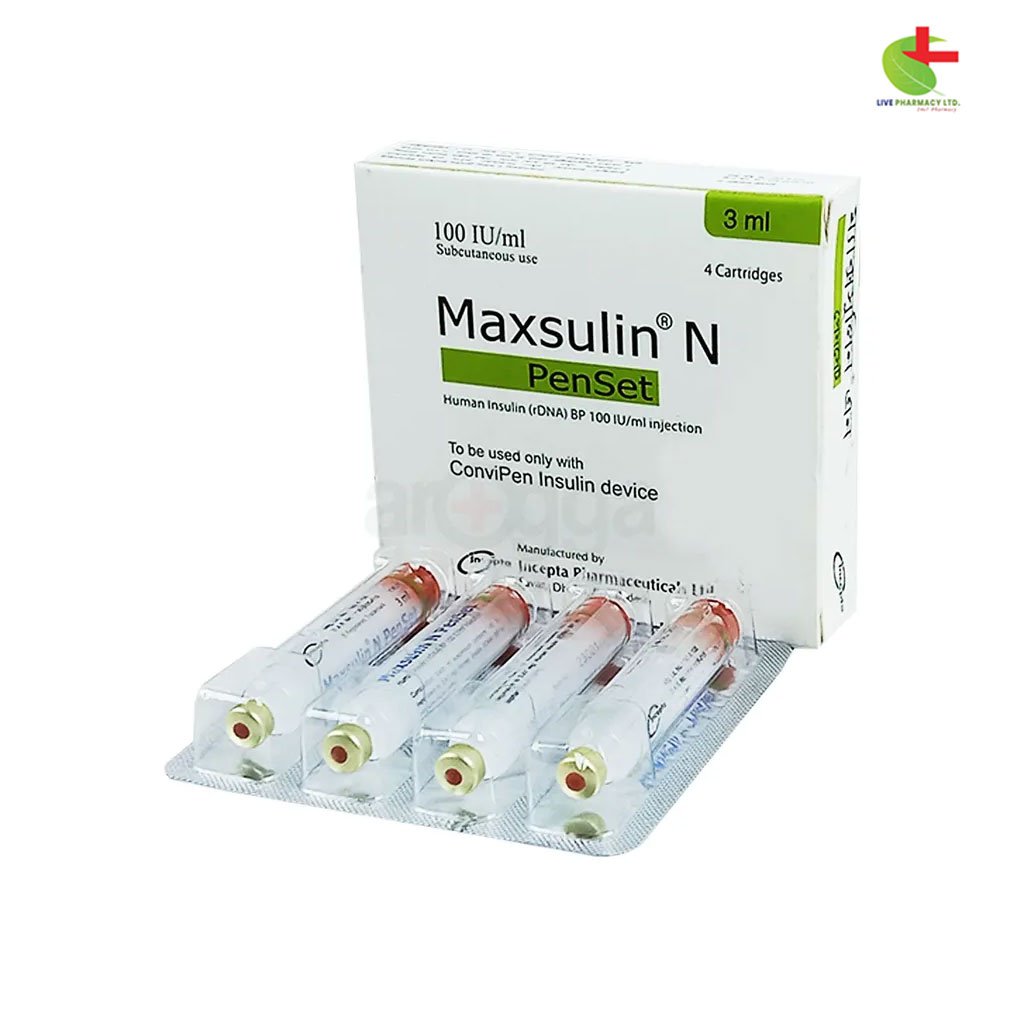
Maxsulin N Penset
222.00৳ Injection
- Maxsulin N Injection is indicated for the treatment of type 1 and type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes, and for stabilization during diabetic emergencies.
- It contains Insulin Human (rDNA) as a fast-acting and medium-acting insulin formulation, providing essential glucose control.
- Administered subcutaneously, its onset of action is within 30 minutes, with a duration of approximately 4-6 hours.
- Proper storage between 2°C and 8°C is crucial to maintain efficacy, with usage guidelines to prevent hypoglycemia and other adverse effects.
 Brand
Brand
|
Incepta Pharmaceuticals Ltd |
|---|---|
 Generics
Generics
|
Insulin Human [rDNA] |
 Type
Type
|
SC Injection |
Indications
Maxsulin N Injection is designed for the following medical purposes:
- Management of Type 1 Diabetes: Effective treatment for all individuals diagnosed with type 1 diabetes.
- Type 2 Diabetes Control: Suitable for patients with type 2 diabetes who have not achieved adequate control through diet or oral hypoglycemic medications.
- Initial Diabetes Stabilization: Used to stabilize diabetes in cases of diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar non-ketotic syndrome, and during critical periods of stress, such as severe infections and major surgical procedures in diabetic patients.
- Gestational Diabetes Treatment: Approved for managing diabetes during pregnancy.
Always consult with a registered healthcare professional before using this medication.
Composition
- Insulin Human R (40 IU/ml): Each milliliter of the solution contains 40 IU (equivalent to 1.388 mg) of Insulin Human (rDNA) USP as Soluble Insulin Human (Regular).
- Insulin Human R (100 IU/ml): Each milliliter contains 100 IU (equivalent to 3.47 mg) of Insulin Human (rDNA) USP as Soluble Insulin Human (Regular).
- Insulin Human N (40 IU/ml): Each milliliter of the suspension contains 40 IU (equivalent to 1.388 mg) of Insulin Human (rDNA) USP as Isophane Insulin Human.
- Insulin Human N (100 IU/ml): Each milliliter contains 100 IU (equivalent to 3.47 mg) of Insulin Human (rDNA) USP as Isophane Insulin Human.
Pharmacology
Maxsulin N Injection is a sterile, clear, colorless solution of Insulin Human. It acts rapidly, providing a relatively short duration of action compared to other insulins. This product can be effectively combined with long-acting insulin formulations. The mechanism of action involves enhancing glucose uptake in muscle and fat cells through insulin receptor binding, while simultaneously inhibiting glucose production in the liver.
- Half-Life: Insulin has a half-life of just a few minutes in the bloodstream with minimal binding to plasma proteins.
- Action Profile After Subcutaneous Injection:
- Onset: Within 30 minutes
- Peak Plasma Levels: Reached between 1 to 3 hours
- Duration: Approximately 4 to 6 hours
Dosage
Dosage should be individualized, determined by a physician based on the patient’s specific needs.
- Type 1 Diabetes: The typical daily insulin requirement for maintenance therapy ranges from 0.5 to 1.0 IU/kg. In pre-pubertal children, this generally varies from 0.7 to 1.0 IU/kg.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Initial doses are usually lower, around 0.3 to 0.6 IU/kg/day.
It is crucial to follow the injection with a meal or snack containing carbohydrates within 30 minutes.
Always consult with a registered healthcare professional before using this medication.
Administration
- Route: Typically administered subcutaneously into the abdominal wall. Other possible injection sites include the thigh, gluteal region, or deltoid area, with subcutaneous abdominal injections providing faster absorption.
- Site Rotation: To prevent lipodystrophy, it is important to rotate injection sites within the same anatomical region.
- Other Administration Methods: Intramuscular and intravenous injections should only be performed under medical supervision.
Dosage Adjustment
- Illness Impact: Conditions like infections and fevers generally increase insulin requirements.
- Renal/Hepatic Impairment: May decrease the need for insulin.
- Lifestyle Changes: Adjustments may be necessary if there are changes in physical activity or diet.
- Transitioning Insulin Preparations: Dosage adjustments may be required when switching between different insulin formulations.
Always consult with a registered healthcare professional before using this medication.
Interactions
Certain medications can affect insulin needs:
- Reduced Insulin Requirement: May be observed with oral hypoglycemic agents (OHA), monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), non-selective beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, salicylates, and alcohol.
- Increased Insulin Requirement: May occur with thiazides, glucocorticoids, thyroid hormones, beta-sympathomimetics, growth hormone, and danazol.
Beta-blockers may mask hypoglycemia symptoms and delay recovery. Both octreotide and lanreotide can have varying effects on insulin requirements. Alcohol may enhance and prolong insulin’s hypoglycemic effects.
Contraindications
Maxsulin N should never be administered to patients experiencing hypoglycemia or those with a known hypersensitivity to human insulin or any of its components.
Side Effects
Adverse reactions to human insulin primarily depend on the dosage and the pharmacological effects. The most common unwanted effect is hypoglycemia, typically occurring if the insulin dosage exceeds the required amount.
Other potential side effects include:
- Lipodystrophy: Can occur at the injection site if proper rotation is not followed.
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Symptoms may include skin rash, itching, sweating, gastrointestinal upset, angioedema, breathing difficulties, palpitations, and low blood pressure, which can be life-threatening.
- Transient Edema: May occur when starting insulin therapy.
Pregnancy & Lactation
Insulin treatment during pregnancy poses no risks to the fetus as it does not cross the placental barrier. Both hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia in inadequately managed diabetes can increase the risk of fetal malformations and mortality. Insulin needs typically decrease in the first trimester and increase during the second and third trimesters. After childbirth, insulin requirements quickly revert to pre-pregnancy levels. Nursing mothers can safely use insulin, though adjustments to dosage and diet may be necessary.
Precautions & Warnings
Inadequate dosing or discontinuation of treatment, especially for type 1 diabetes, can lead to hyperglycemia, which may result in diabetic ketoacidosis—a potentially life-threatening condition.
Hypoglycemia may occur if the insulin dose exceeds what is necessary.
Transferring a patient to a different type or brand of insulin should only be done under strict medical supervision. Variations in insulin strength, brand, type, or source may necessitate dosage changes.
Travelers across time zones should consult their physician, as adjustments to insulin administration and meal timing may be required.
Overdose Effects
Maxsulin N does not have specific overdose definitions, but hypoglycemia may progress through stages:
- Mild Episodes: Can be treated with oral glucose or sugary products.
- Severe Episodes: Require immediate treatment with glucagon (0.5 to 1 mg) administered intramuscularly or subcutaneously by a trained individual or intravenous glucose by a healthcare professional. If the patient does not respond to glucagon within 10 to 15 minutes, intravenous glucose is necessary.
Once consciousness is regained, oral carbohydrates are recommended to prevent relapse.
Therapeutic Class
Medium-Acting Insulin
Storage Conditions
Maxsulin N should be stored between 2°C and 8°C (in the refrigerator). Any Maxsulin N preparations that have been frozen must not be used. These preparations should be kept in their outer carton to shield them from light and protected from excessive heat or direct sunlight. Solutions should not be used if they appear cloudy or discolored. Once in use, a vial can be stored below 25°C for up to 6 weeks or below 30°C for up to 4 weeks.










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.