
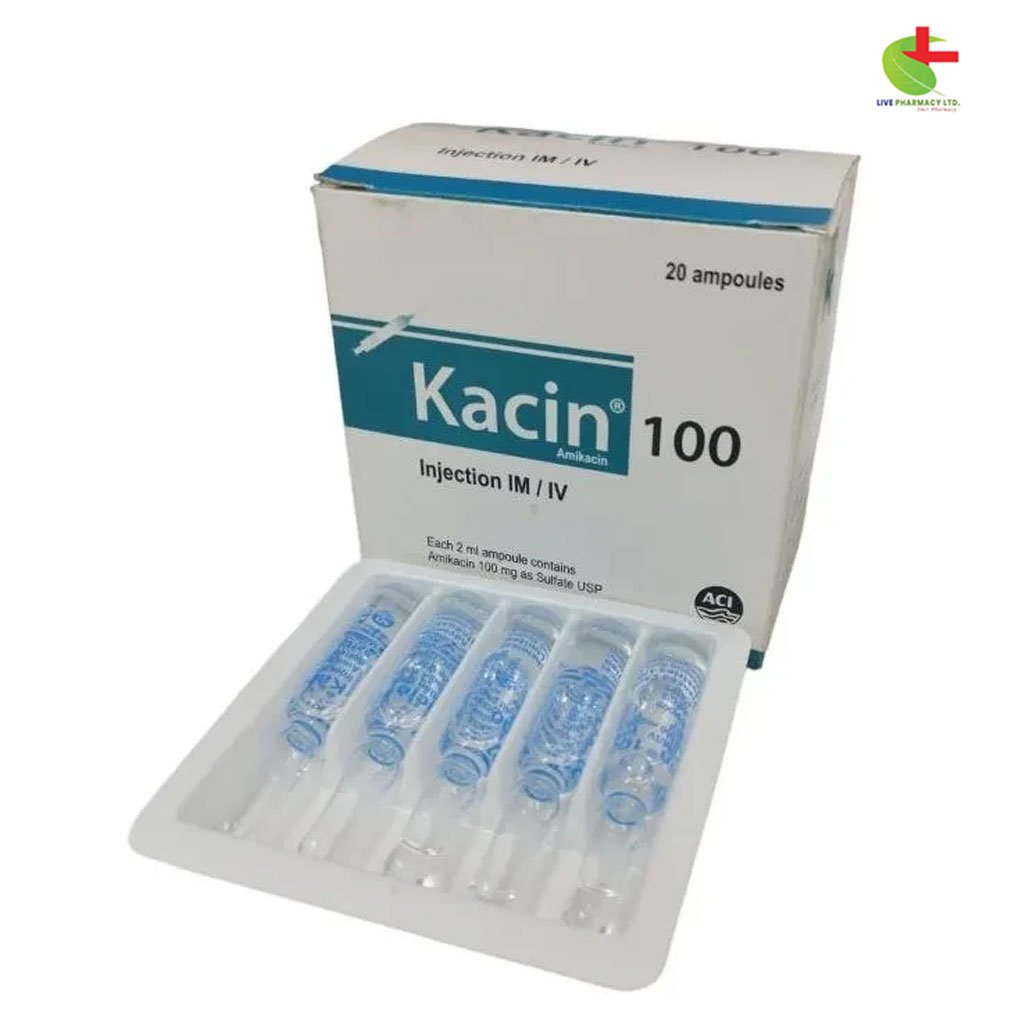
Kacin 100
200.00৳ Strip(10)
- Kacin is an effective aminoglycoside antibiotic used for treating severe infections caused by Gram-negative bacteria, including septicemia, respiratory tract infections, and urinary tract infections.
- It is also effective against Gentamicin and Tobramycin-resistant organisms like Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Serratia marcescens.
- Kacin is used in serious staphylococcal infections and can be considered as initial therapy for suspected mixed infections.
- The drug is administered either intramuscularly or intravenously, with dosage adjustments based on age, renal function, and the severity of the infection.
 Brand
Brand
|
ACI Limited |
|---|---|
 Generics
Generics
|
Amikacin |
 Type
Type
|
IM/IV Injection |
Indications
Kacin is indicated for the short-term management of severe infections caused by susceptible strains of Gram-negative bacteria. It is particularly effective in treating bacterial septicemia, including neonatal sepsis, as well as serious infections affecting the respiratory tract, bones, joints, central nervous system (such as meningitis), skin, soft tissues, and intra-abdominal infections (including peritonitis). Kacin also plays a key role in treating burns, postoperative infections (including those following vascular surgery), and complicated, recurrent urinary tract infections caused by resistant organisms.
Kacin is effective against infections caused by Gentamicin and/or Tobramycin-resistant strains of Gram-negative organisms like Proteus rettgeri, Providencia stuartii, Serratia marcescens, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Additionally, Kacin is used in treating staphylococcal infections, often as an initial therapy for severe infections where both Gram-negative bacteria and staphylococci may be present.
Pharmacology
Amikacin Sulfate, a semi-synthetic aminoglycoside antibiotic, is effective in vitro against a wide range of pathogens, including Pseudomonas species, Escherichia coli, Proteus species, Providencia species, Klebsiella-Enterobacter species, Acinetobacter species, and Citrobacter freundii. Even when other aminoglycosides like Gentamicin, Tobramycin, and Kanamycin show resistance, many of these organisms remain susceptible to Amikacin. It is also potent against penicillinase and non-penicillinase-producing Staphylococcus species, including methicillin-resistant strains.
Dosage
- Adults and Children: 15 mg/kg/day, divided into two equal doses (equivalent to 500 mg twice daily for adults). For accurate dosing in children, the 100 mg form is recommended.
- Neonates and Premature Children: Initial loading dose of 10 mg/kg, followed by 15 mg/kg/day in two equally divided doses.
- Elderly: Due to renal excretion, renal function must be monitored, and dosage adjusted accordingly for impaired renal function.
For life-threatening infections or those caused by Pseudomonas, the adult dosage may be increased to 500 mg every eight hours, with a maximum daily dose of 1.5 g and a treatment duration not exceeding 10 days. The total adult dose should not exceed 15 g.
- Urinary Tract Infections (non-pseudomonal): 7.5 mg/kg/day in two equally divided doses (equivalent to 250 mg twice daily for adults).
- Impaired Renal Function: The daily dose should be reduced, and dosing intervals extended to prevent drug accumulation.
Administration
- Intramuscular or Intravenous: The intramuscular route is preferred for most infections. However, in cases of life-threatening infections or when intramuscular injections are not feasible, intravenous administration may be considered.
- Intraperitoneal Use: After recovery from anesthesia, Amikacin may be used as an irrigant at a concentration of 0.25%.
Interactions
Co-administration of Kacin with muscle relaxants may enhance their effects, potentially leading to respiratory depression. Using Kacin with other aminoglycosides should be avoided due to an increased risk of ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity. Combining Kacin with fast-acting diuretics can elevate the risk of ototoxicity, especially in patients with renal failure. Concomitant use with Cephalosporins or Polymixins also increases nephrotoxicity risk.
Contraindications
Kacin is contraindicated in individuals with a known hypersensitivity to Amikacin or any components of the injection.
Side Effects
Common adverse effects include tinnitus, vertigo, partial reversible or irreversible hearing loss, skin rash, drug-induced fever, headache, paresthesia, nausea, and vomiting.
Pregnancy & Lactation
Amikacin crosses the placenta and enters fetal circulation, potentially causing ototoxicity in the fetus. There is insufficient data regarding its safety during breastfeeding.
Precautions & Warnings
Given its concentration in the renal excretory system, it is essential for patients to remain well-hydrated to minimize renal tubule irritation. If azotemia increases, treatment should be discontinued. Regular monitoring of renal function is critical during Amikacin treatment.
Use in Special Populations
- Pediatrics: The safety and efficacy of Kacin in children under 16 years of age have not been established.
- Overdose: In the event of overdose or toxic reactions, peritoneal dialysis or hemodialysis can aid in the removal of Amikacin from the bloodstream.
Therapeutic Class
Aminoglycosides.
Storage Conditions
Store below 30°C, away from light and moisture. Keep out of reach of children.










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.