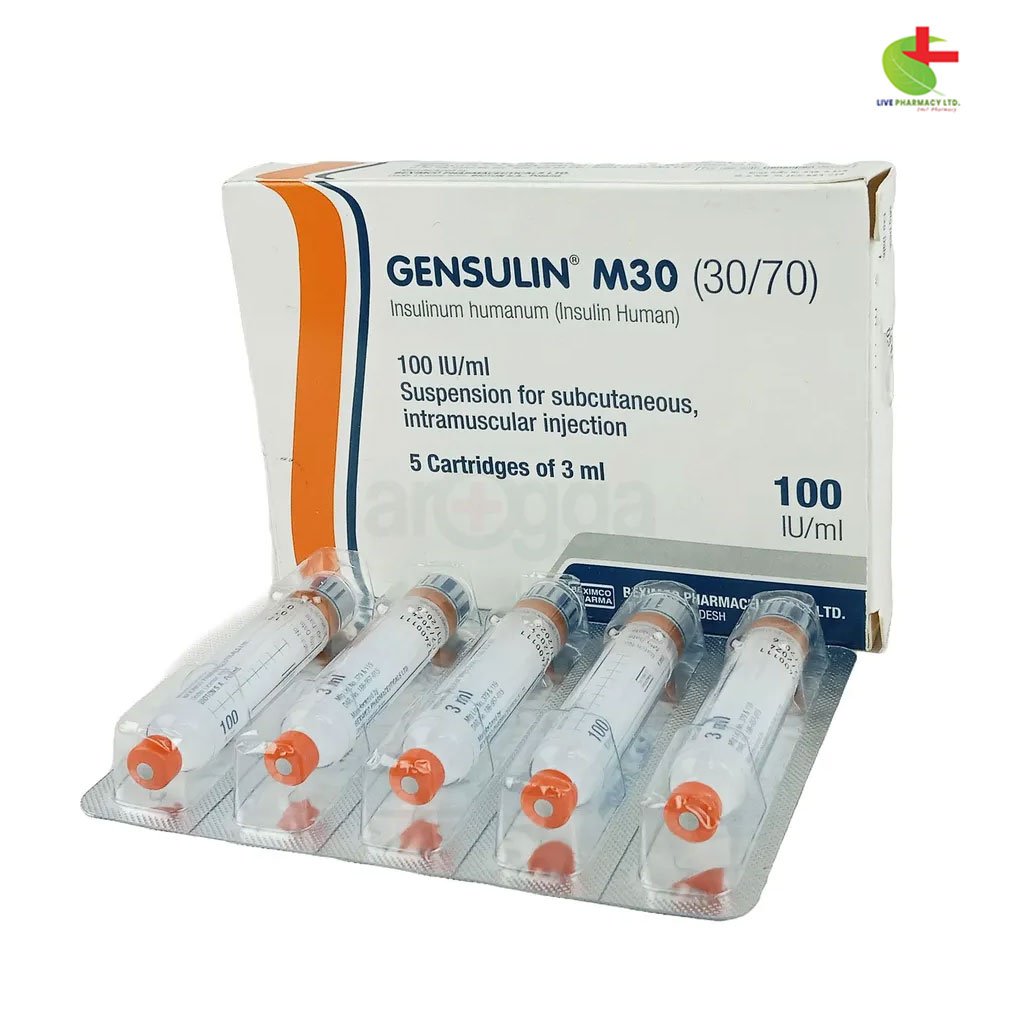
Gensulin M30 Cartidge
222.00৳ Injection - (100IU/ml)
- Indications: Ideal for managing type 1 and type 2 diabetes, stabilizing during acute conditions, and treating gestational diabetes.
- Composition: Gensulin M30 Cartridge contains 100 IU/ml of human insulin, with 30% Regular Insulin and 70% Isophane Insulin.
- Pharmacology: Starts working within 30 minutes, peaks between 1-3 hours, and lasts for 18-24 hours, helping control blood glucose levels.
- Dosage: Tailored by a physician; typical daily dosage for type 1 diabetes is 0.5-1.0 IU/kg, and for type 2 diabetes, it’s 0.3-0.6 IU/kg.
 Brand
Brand
|
Beximco Pharmaceuticals Ltd |
|---|---|
 Generics
Generics
|
Regular Insulin Human + Isophane Insulin Human |
 Type
Type
|
SC Injection |
0
People watching this product now!
Description
Indications
- Type 1 Diabetes Management: Suitable for treating all patients diagnosed with type 1 diabetes.
- Type 2 Diabetes Control: Ideal for patients with type 2 diabetes who do not achieve adequate control with diet alone or oral hypoglycemic medications.
- Initial Stabilization: Effective for stabilizing diabetes in patients with diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar non-ketotic syndrome, or during stress conditions such as severe infections and major surgeries.
- Gestational Diabetes: Useful for managing diabetes that occurs during pregnancy.
Composition
- 30/70 Formula: Each milliliter of suspension contains 100 IU (equivalent to 3.47 mg) of Human Insulin (rDNA) USP, with a composition of 30% Regular Insulin and 70% Isophane Insulin.
- 50/50 Formula: Each milliliter of suspension contains 100 IU (equivalent to 3.47 mg) of Human Insulin (rDNA) USP, with a composition of 50% Regular Insulin and 50% Isophane Insulin.
Pharmacology
Insulin lowers blood glucose levels by facilitating glucose uptake into muscle and fat cells and inhibiting glucose production by the liver. It has a short half-life of a few minutes and does not bind significantly to plasma proteins. After subcutaneous injection, insulin typically shows:
- Onset of Action: Within 30 minutes
- Peak Plasma Levels: Reached between 1-3 hours
- Duration of Action: Approximately 18-24 hours
Dosage
- Individualized Treatment: Dosage should be tailored by a healthcare provider to meet the patient’s needs.
- Type 1 Diabetes: The average daily insulin requirement ranges from 0.5 to 1.0 IU/kg, with variations in pre-pubertal children from 0.7 to 1.0 IU/kg.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Initial doses are generally lower, around 0.3 to 0.6 IU/kg/day.
- Meal Timing: Injections should be followed by a meal or snack containing carbohydrates within 30 minutes.
Administration
- Injection Sites: Administer subcutaneously in the abdominal wall for faster absorption; other sites include the thigh, gluteal region, or deltoid region.
- Site Rotation: To prevent lipodystrophy, rotate injection sites within the anatomical area.
Dosage Adjustment
- Illness and Conditions: Concomitant illnesses such as infections or fever, renal or hepatic impairment, changes in physical activity, or diet can affect insulin requirements.
- Insulin Type Changes: Adjust dosage when switching between different insulin preparations.
Preparation and Usage
- Pre-Use Check: Ensure correct insulin type, inspect the cartridge and rubber plunger, and disinfect the rubber membrane.
- Do Not Use: If the cartridge is damaged, improperly stored, or if the insulin is not uniformly white and cloudy.
- Mixing: Gently roll the cartridge to mix thoroughly before each use until the solution appears uniformly white and cloudy.
- Injection Technique: Inject insulin using the method described in the delivery system manual, keeping the needle under the skin for at least 6 seconds to ensure complete dose delivery.
Interaction
- Reduced Insulin Requirements: Oral hypoglycemic agents, MAO inhibitors, non-selective beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, salicylates, and alcohol may lower insulin needs.
- Increased Insulin Requirements: Thiazides, glucocorticoids, thyroid hormones, beta-sympathomimetics, growth hormone, and Danazol may raise insulin requirements.
- Hypoglycemia: Beta-blockers can mask hypoglycemia symptoms, while octreotide and lanreotide may both increase and decrease insulin needs.
Contraindications
- Do Not Use: In cases of hypoglycemia or hypersensitivity to human insulin or any excipients.
Side Effects
- Common Effects: Hypoglycemia, which can occur if the dose exceeds insulin needs, and lipodystrophy from not rotating injection sites.
- Severe Reactions: Generalized hypersensitivity, including rash, itching, and in severe cases, angioneurotic edema and difficulty breathing. Edema may occur upon initiation of therapy but is usually transient.
Pregnancy & Lactation
- Pregnancy: Insulin treatment is safe during pregnancy as it does not cross the placental barrier. Insulin requirements may decrease in the first trimester and increase in later trimesters.
- Lactation: Insulin treatment during breastfeeding poses no risk to the baby, although adjustments to dosage and diet may be necessary.
Precautions & Warnings
- Hyperglycemia Risk: Inadequate dosing or discontinuation can lead to hyperglycemia and diabetic ketoacidosis, especially in type 1 diabetes.
- Dosage Changes: Transfers between different insulin types or brands should be supervised by a healthcare provider. Consult a doctor before traveling across time zones.
Overdose Effects
- Mild Hypoglycemia: Treated with oral glucose or sugary products.
- Severe Hypoglycemia: Requires glucagon or intravenous glucose administration.
Storage Conditions
- Storage: Keep insulin between 2°C and 8°C. Do not use if frozen. Protect from light and excessive heat. Once in use, store below 25°C for up to 6 weeks or below 30°C for up to 4 weeks. Mix by rolling the cartridge before use.
Reviews (0)
Be the first to review “Gensulin M30 Cartidge” Cancel reply
About brand
Shipping & Delivery










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.