
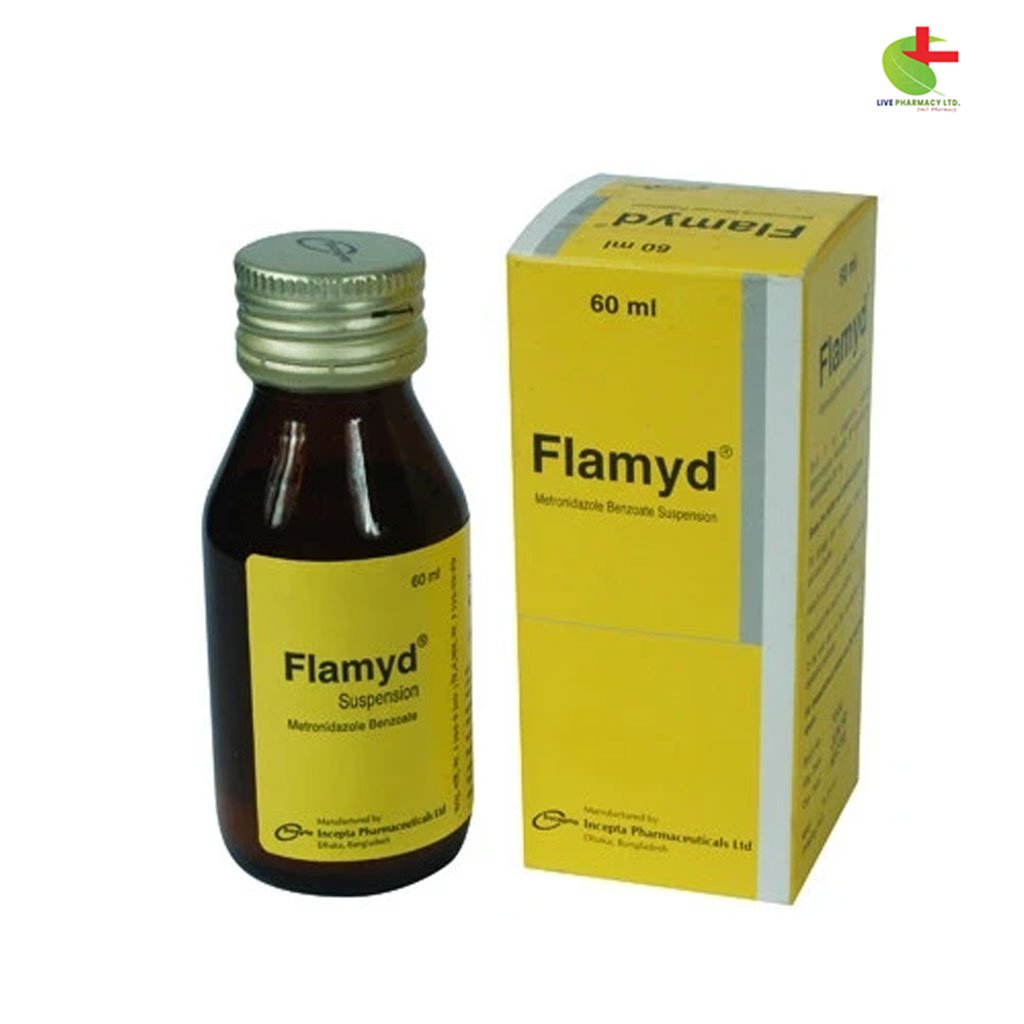
Flamyd Suspension
35.00৳ Bottle (60ml)
- Flamyd is an antiprotozoal medication primarily containing Metronidazole, indicated for various infections caused by anaerobic bacteria, including trichomoniasis and amoebiasis.
- It is effective in treating conditions like bacterial vaginosis, acute ulcerative gingivitis, and anaerobically infected wounds.
- Available in tablet, suspension, vaginal gel, suppository, and IV infusion forms, Flamyd dosage varies by age and condition.
- Caution is advised in patients with hepatic impairment and those taking disulfiram or anticoagulants.
- Always use under medical supervision and follow recommended guidelines.
 Brand
Brand
|
Incepta Pharmaceuticals Ltd |
|---|---|
 Generics
Generics
|
Metronidazole |
 Type
Type
|
Oral Suspension |
Indications
Flamyd is prescribed for the treatment of various conditions, including:
- Prevention of Post-Operative Infections: Effective against anaerobic bacteria, particularly Bacteroides species and anaerobic streptococci.
- Treatment of Serious Infections: Addresses septicaemia, bacteraemia, peritonitis, brain abscesses, pelvic abscesses, pelvic cellulitis, and post-operative wound infections caused by anaerobes.
- Urogenital Infections: Used in the management of trichomoniasis.
- Bacterial Vaginosis: Also referred to as non-specific vaginitis.
- Amoebiasis: Treats all forms, including intestinal and extra-intestinal diseases, as well as asymptomatic cyst carriers.
- Giardiasis: Effective against Giardia infections.
- Acute Ulcerative Gingivitis: Manages symptoms in both adults and children.
- Anaerobically Infected Ulcers: Useful for treating leg ulcers and pressure sores.
- Acute Dental Infections: Targets infections caused by anaerobic organisms.
- Antibiotic-Associated Pseudomembranous Colitis: Provides relief for this condition.
Always consult a registered physician before taking medication.
Pharmacology
Flamyd contains Metronidazole, an antiprotozoal agent belonging to the imidazole class of antibacterial drugs. The drug’s 5-nitro group is reduced metabolically by anaerobic bacteria, forming a reactive compound that interacts with DNA, leading to its bactericidal effects.
Dosage and Administration
Tablets and Suspension:
Trichomoniasis:
- Adults & Children (10+ years):
- 200 mg three times daily (tid) or 400 mg twice daily (bid) for 7 days.
- 800 mg in the morning and 1-2 g at night for 2 days.
- 2 g as a single dose for 1 day.
- Children:
- Ages 7-10 years: 100 mg tid.
- Ages 3-7 years: 100 mg bid.
- Ages 1-3 years: 50 mg tid.
Intestinal Amoebiasis:
- Adults & Children (10+ years): 800 mg tid for 5 days.
- Children:
- Ages 7-10 years: 400 mg tid.
- Ages 3-7 years: 200 mg four times daily (qid).
- Ages 1-3 years: 200 mg tid.
Extra-Intestinal & Asymptomatic Amoebiasis:
- Adults & Children (10+ years): 400-800 mg tid for 5-10 days.
- Children:
- Ages 7-10 years: 200-400 mg tid.
- Ages 3-7 years: 100-200 mg qid.
- Ages 1-3 years: 100-200 mg tid.
Giardiasis:
- Adults & Children (10+ years): 2 g once daily for 3 days.
- Children:
- Ages 7-10 years: 1 g once daily.
- Ages 3-7 years: 600-800 mg once daily.
- Ages 1-3 years: 500 mg once daily.
Acute Ulcerative Gingivitis:
- Adults & Children (10+ years): 200 mg tid for 3 days.
- Children:
- Ages 7-10 years: 100 mg tid.
- Ages 3-7 years: 100 mg bid.
- Ages 1-3 years: 50 mg tid.
Acute Dental Infections:
- Adults & Children (10+ years): 200 mg tid for 3-7 days.
Bacterial Vaginosis:
- Adults & Children (10+ years): 400 mg bid for 7 days or 2 g as a single dose for 1 day.
Leg Ulcers and Pressure Sores:
- Adults & Children (10+ years): 400 mg tid for 7 days.
Anaerobic Infections:
- Adults: 800 mg initially, then 400 mg tid for 7 days.
- Children: 7.5 mg/kg tid for ages 1-10 years.
Surgical Prophylaxis:
- Adults: 400 mg tid starting 24 hours before surgery for 1 day.
- Children: 7.5 mg/kg tid for ages 1-10 years.
Vaginal Gel: The recommended dose is one full applicator of Metronidazole gel (approximately 5 grams containing 37.5 mg of Metronidazole) administered intravaginally once or twice a day for 5 days. For once daily dosing, it should be applied at bedtime.
Suppository:
For Anaerobic Infections:
- Adults: 1 g every 8 hours for 3 days, then 1 g every 12 hours.
- Children: Ages 5-10 years: 500 mg every 8 hours for 3 days, then every 12 hours; for those over 10 years, use adult dosage.
For Surgical Prophylaxis:
- Adults: 1 g 2 hours before surgery; up to 3 additional doses of 1 g every 8 hours for high-risk procedures.
- Children: Ages 5-10 years: 500 mg 2 hours before surgery; up to 3 additional doses of 500 mg every 8 hours for high-risk procedures.
IV Infusion: Metronidazole intravenous infusion does not require dilution and should not be mixed with other medications before administration.
- Adults and Children (12+ years): Infuse 500 mg every 8 hours at a rate of 5 ml/minute, with a maximum of 4 g in 24 hours. Treatment duration is typically 7 days, but may be extended for reinfection cases. For surgical prophylaxis, administer shortly before surgery and continue with 8-hourly doses for 24 hours.
- Children (under 12 years): 7.5 mg/kg body weight/day every 8 hours at a rate of 5 ml/minute.
Always consult a registered physician before taking medication.
Interactions
- Disulfiram: Concurrent use can lead to psychotic reactions.
- Alcohol: Avoid alcohol during treatment and for at least one day afterward to prevent disulfiram-like reactions (flushing, vomiting, tachycardia).
- Oral Anticoagulants (Warfarin): May enhance anticoagulant effects, necessitating increased monitoring of prothrombin time and potential adjustments in therapy.
- Lithium: May elevate lithium plasma levels.
- Cyclosporin: Close monitoring of serum levels is required during co-administration.
- Phenytoin or Phenobarbital: These can increase the elimination of Flamyd, reducing plasma levels.
- 5-Fluorouracil: May reduce clearance, increasing the toxicity of 5-fluorouracil.
- Busulfan: Can increase plasma levels, leading to potential toxicity.
Contraindications
Flamyd is contraindicated for individuals with a known hypersensitivity to Metronidazole or other Nitroimidazole derivatives.
Side Effects
Common side effects may include a metallic taste, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, drowsiness, and skin rashes.
Pregnancy and Lactation
Flamyd is classified as a US FDA Pregnancy Category B medication. While there are no well-controlled studies in pregnant women, this drug should only be used during pregnancy if absolutely necessary. Metronidazole can be excreted in human milk, so caution is advised when administering it to nursing mothers.
Precautions and Warnings
- If Flamyd must be taken for longer than the typical duration, regular hematological testing (especially leukocyte count) is advised, and patients should be monitored for adverse effects such as peripheral or central neuropathy (e.g., paresthesia, ataxia, dizziness, seizures).
- Caution is advised for patients with hepatic encephalopathy, as Flamyd may darken urine.
Use in Special Populations
- Hepatic Impairment: Since Flamyd is primarily metabolized by the liver, clearance may be significantly impaired in advanced hepatic insufficiency. Dosage may need to be reduced to one-third of the standard dose, administered once daily.
- Renal Impairment: The elimination half-life remains unchanged; therefore, dosage adjustments are not necessary. However, metabolites may accumulate in patients with renal failure. Following hemodialysis, re-administer Flamyd immediately.
Overdose Effects
Overdoses of up to 12 g have been reported, primarily resulting in vomiting, ataxia, and slight disorientation. There is no specific antidote; treatment should focus on symptomatic and supportive care.
Therapeutic Class
- Amoebicides
- Anti-diarrheal
- Antiprotozoal
Storage Conditions
Store Flamyd below 30°C, away from light, and out of reach of children. Do not use past the expiration date.











Reviews
There are no reviews yet.