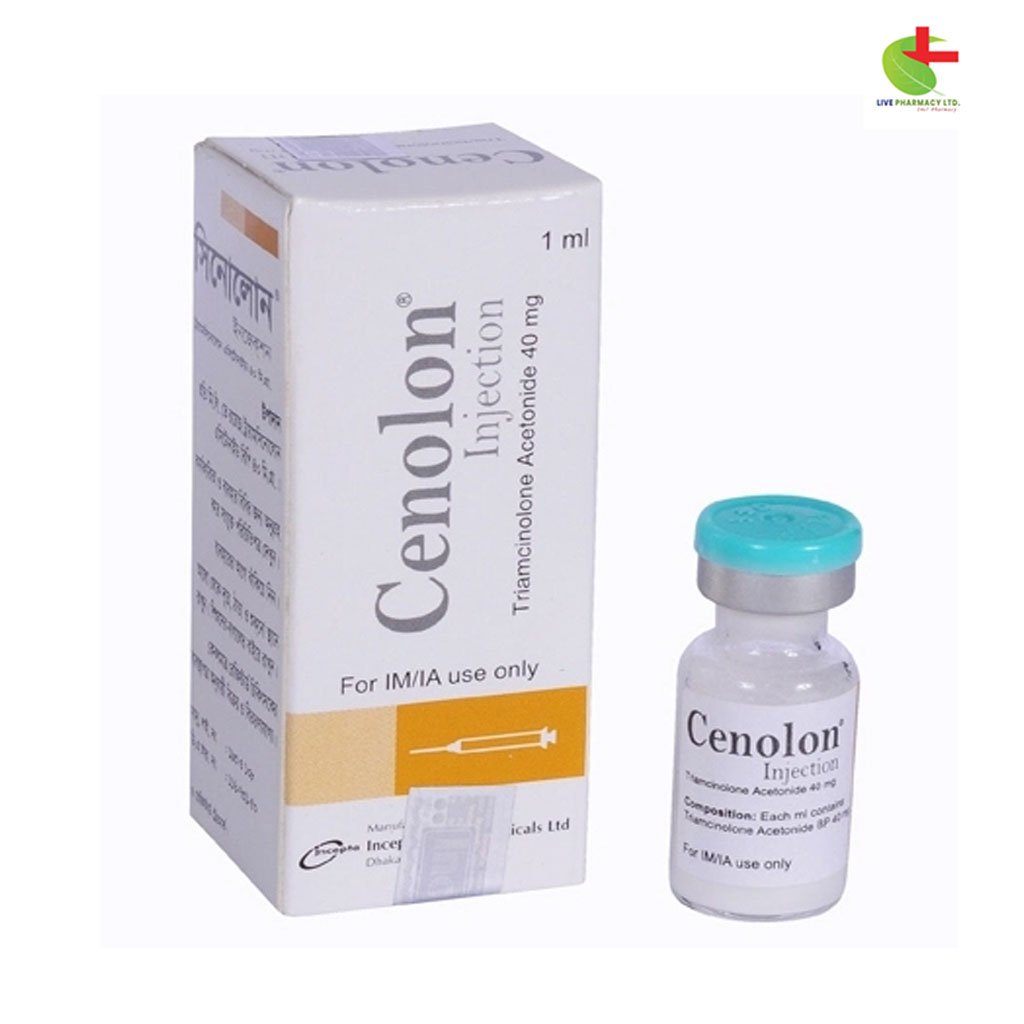
Cenolon Injection
75.00৳ Injection
- Cenolon injection contains Triamcinolone Acetonide, a synthetic glucocorticoid corticosteroid with anti-inflammatory properties.
- It is indicated for various conditions, including rheumatic disorders, allergic states, dermatologic diseases, and endocrine disorders.
- Administered intramuscularly or intra-articularly, Cenolon is effective in managing acute episodes of inflammatory conditions.
- Caution is advised regarding potential side effects and contraindications, particularly in patients with hypersensitivity or certain health conditions.
 Brand
Brand
|
Incepta Pharmaceuticals Ltd |
|---|---|
 Generics
Generics
|
Triamcinolone Acetonide |
 Type
Type
|
IM/IA Injection |
0
People watching this product now!
Description
Cenolon Injection (Triamcinolone Acetonide)
Indications
Intramuscular Use:
- Rheumatic Disorders:
- Acute gouty arthritis
- Acute rheumatic carditis
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis (including juvenile)
- Allergic States:
- Severe allergic conditions (asthma, atopic dermatitis, etc.)
- Dermatologic Diseases:
- Bullous dermatitis herpetiformis
- Pemphigus
- Severe erythema multiforme
- Endocrine Disorders:
- Adrenocortical insufficiency
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- Gastrointestinal Diseases:
- Regional enteritis
- Ulcerative colitis
- Hematologic Disorders:
- Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
- Diamond-Blackfan anemia
- Neoplastic Diseases:
- Palliative management of leukemias and lymphomas
- Nervous System:
- Acute exacerbations of multiple sclerosis
- Cerebral edema from brain tumors
- Ophthalmic Diseases:
- Sympathetic ophthalmia
- Uveitis
- Renal Diseases:
- Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome
- Respiratory Diseases:
- Berylliosis
- Symptomatic sarcoidosis
- Miscellaneous:
- Tuberculous meningitis with appropriate therapy
Intra-articular Use:
- Adjunctive therapy for:
- Acute gouty arthritis
- Bursitis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
Pharmacology
- Composition: Triamcinolone Acetonide is a synthetic glucocorticoid with anti-inflammatory properties.
- Absorption: Well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Extended duration of effect (up to several weeks).
- Adrenal Suppression: Occurs within 24-48 hours post-injection, returning to normal in 30-40 days.
Dosage & Administration
- General: Initial doses range from 2.5 mg to 100 mg, adjusted based on response.
- Systemic Administration:
- Adults: Initial dose of 60 mg into the gluteal muscle, with adjustments typically between 40-80 mg.
- Pediatric: 0.11 to 1.6 mg/kg/day in 3-4 doses.
- Local Administration (Intra-articular):
- Initial dose: 2.5 mg to 15 mg depending on joint size.
- Up to 40 mg for larger areas may be sufficient.
Interactions
- Aminoglutethimide: May reduce corticosteroid-induced adrenal suppression.
- Anticoagulants (e.g., Warfarin): Monitor coagulation indices closely.
- Diuretics: Risk of hypokalemia when used with corticosteroids.
- Antidiabetics: Adjustments may be necessary due to increased blood glucose.
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to any components.
- Contraindicated in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Side Effects
- Allergic Reactions: Anaphylaxis, angioedema.
- Cardiovascular: Hypertension, arrhythmias, congestive heart failure.
- Dermatologic: Acne, rash, skin thinning.
- Endocrine: Cushingoid state, menstrual irregularities.
- Fluid/Electrolyte Disturbances: Fluid retention, hypokalemia.
- Gastrointestinal: Nausea, pancreatitis, peptic ulcers.
- Musculoskeletal: Osteoporosis, muscle weakness.
- Neurologic/Psychiatric: Mood swings, insomnia, increased intracranial pressure.
- Ophthalmic: Glaucoma, cataracts.
Pregnancy & Lactation
- Category C: Use only if benefits justify potential risks. Appears in human milk; may affect growth and endogenous production.
Precautions & Warnings
- Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration necessary.
- Gradual reduction of dosage when applicable.
- Monitor for complications related to dose and treatment duration.
Consultation Note
Always follow the advice of a registered physician when administering this medication.
Reviews (0)
Be the first to review “Cenolon Injection” Cancel reply
About brand
Shipping & Delivery










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.