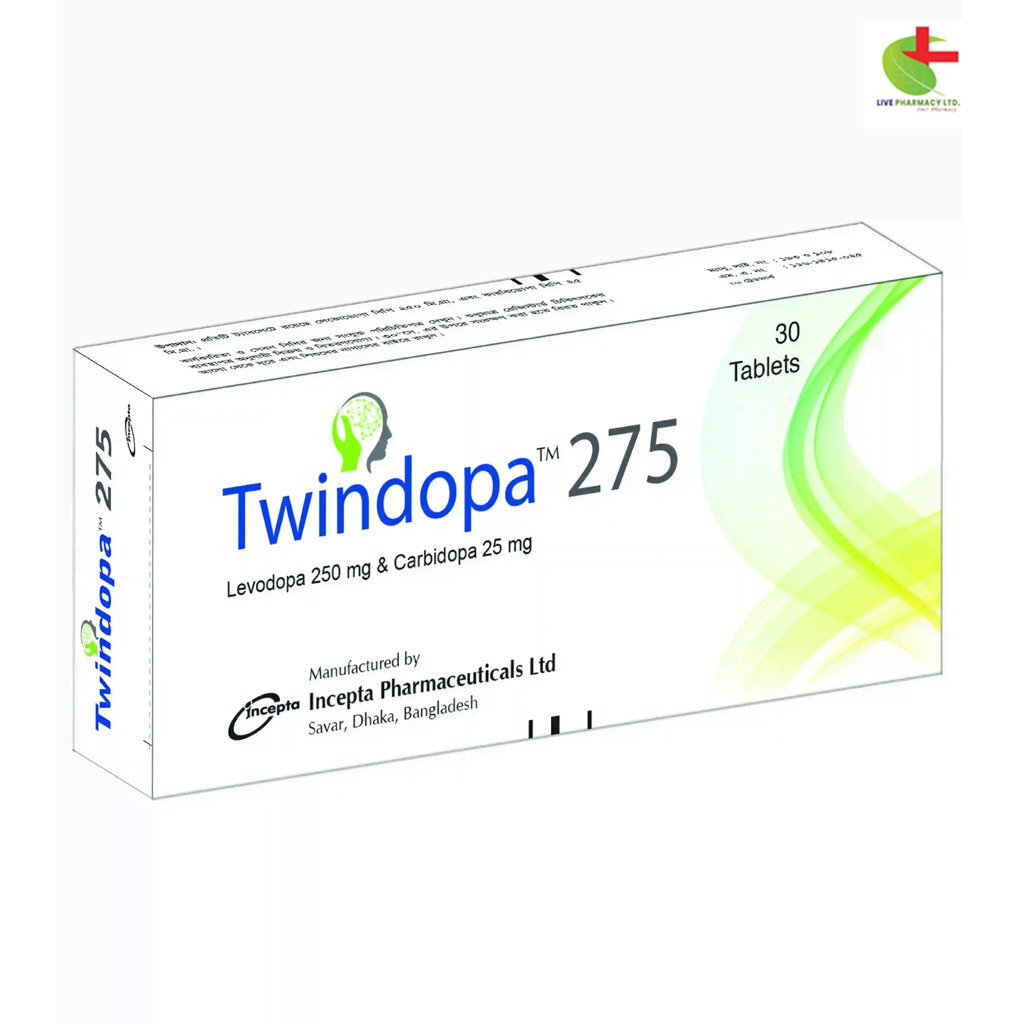
Twindopa 275
100.00৳ strip
- Carbidopa-Levodopa treats Parkinson’s disease and related syndromes.
- Alleviates symptoms such as rigidity, tremors, and bradykinesia.
- Increases dopamine levels in the brain to improve motor function.
- Supports recovery after a stroke.
- Use only under the guidance of a healthcare professional for optimal results.
 Brand
Brand
|
Incepta Pharmaceuticals Ltd |
|---|---|
 Generics
Generics
|
Levodopa + Carbidopa |
 Type
Type
|
Tablet |
Indications for Use
This medication is primarily prescribed for managing Parkinson’s disease and its related syndromes. It helps alleviate several symptoms of parkinsonism, particularly rigidity and bradykinesia. Additionally, it is effective in managing tremors, dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), sialorrhea (excessive drooling), and postural instability commonly associated with Parkinson’s disease. When combined with physiotherapy, Levodopa and Carbidopa have been shown to enhance motor recovery following a stroke.
Note: Always take this medication as directed by a licensed healthcare professional.
Product Description
Levodopa, a metabolic precursor to dopamine, effectively crosses the blood-brain barrier and is converted into dopamine within the brain. Carbidopa, a dopa decarboxylase (DDC) inhibitor, works by reducing the breakdown of Levodopa outside the brain, ensuring that more Levodopa is available for conversion into dopamine within the brain.
Dosage & Administration
For 100/10 mg Tablets:
- Initial Dose: Start with one tablet three or four times a day. In some cases, an increase in dosage may be necessary to achieve the best results.
- Titration: Gradually increase the dosage by one tablet every day or every other day until the desired therapeutic effect is reached, up to a maximum of eight tablets (two tablets four times daily).
For 250/25 mg Tablets:
- Initial Dose: Begin with half a tablet, taken once or twice daily. Adjust the dose as needed to reach the optimal therapeutic response, with increments of half a tablet daily or every other day.
- Suggested Starting Dosage: For patients requiring more than 1500 mg of Levodopa daily, the starting dose is one 250/25 mg tablet three to four times a day.
Maintenance Dose:
- Adjust the dosage to meet individual therapeutic needs. If higher Levodopa doses are required, substitute with the 250/25 mg tablet at one tablet three or four times a day. Dosage may be gradually increased by half to one tablet every other day, up to a maximum of eight tablets daily. Note that total daily doses exceeding 200 mg of Carbidopa are not commonly recommended.
Always follow the advice of a registered healthcare professional.
Drug Interactions
- Antihypertensive Medications: When starting Carbidopa-Levodopa therapy, patients on antihypertensive medications may experience symptomatic postural hypotension. Dosage adjustments of antihypertensive drugs may be necessary.
- Antidepressants: Concurrent use with tricyclic antidepressants may lead to rare side effects, such as hypertension and dyskinesia.
- Iron Supplements: The absorption of Carbidopa-Levodopa can be reduced when taken alongside iron salts (e.g., ferrous sulfate or ferrous gluconate).
- Dopamine Antagonists: Medications like phenothiazines, butyrophenones, and risperidone may decrease the effectiveness of Levodopa.
- Selegiline: Combining Carbidopa-Levodopa with selegiline may cause severe orthostatic hypotension (a drop in blood pressure upon standing).
Patients should be closely monitored for changes in therapeutic response when combining these medications.
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity: Do not use if you are allergic to Carbidopa or Levodopa.
- Narrow-Angle Glaucoma: This medication is contraindicated in patients with narrow-angle glaucoma.
- Malignant Melanoma: As Levodopa may activate malignant melanoma, it is not recommended for use in patients with suspicious skin lesions or a history of melanoma.
Side Effects
Common side effects often result from dopamine’s central neuropharmacological activity. Reducing the dosage can typically alleviate these symptoms. Notable adverse effects include:
- Neurological: Dyskinesia (e.g., choreiform and dystonic movements), dizziness, hallucinations, confusion, depression, somnolence (drowsiness), and increased libido.
- Cardiovascular: Orthostatic hypotension (low blood pressure when standing), palpitations, and chest pain.
- Gastrointestinal: Nausea, vomiting, dark saliva, gastrointestinal bleeding, diarrhea, and ulcers.
- Hematologic: Anemia (both hemolytic and non-hemolytic), thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, and agranulocytosis.
- Skin & Allergic Reactions: Rash, alopecia (hair loss), dark sweat, urticaria (hives), and angioedema (swelling of the deeper layers of the skin).
- Respiratory: Difficulty breathing (dyspnea).
- Urinary: Dark urine.
If any of these symptoms worsen or are bothersome, consult your doctor promptly.
Pregnancy & Lactation
Carbidopa-Levodopa has not been studied in pregnant women, but animal studies show that Levodopa and its combinations may cause skeletal and visceral malformations in rabbits. Therefore, its use during pregnancy should only be considered if the potential benefits outweigh the risks.
It is unknown whether Carbidopa is excreted in human milk. Due to the risk of serious side effects in nursing infants, a decision should be made to either discontinue breastfeeding or discontinue Carbidopa-Levodopa, depending on the importance of the medication to the mother.
Precautions & Warnings
- Psychiatric Conditions: Use caution in patients with a history of psychosis, as Carbidopa-Levodopa can worsen psychiatric symptoms.
- Cardiovascular Issues: Patients with severe heart conditions, including arrhythmias, should be monitored carefully, especially during initial treatment.
- Glaucoma: Patients with chronic wide-angle glaucoma may use this medication cautiously, provided intraocular pressure is well-controlled.
Careful monitoring is necessary when administering this medication to patients with a history of gastrointestinal disorders, endocrine diseases, or convulsions.
Use in Special Populations
- Children: The safety and effectiveness of Carbidopa-Levodopa in children under the age of 18 have not been established. Therefore, its use is not recommended in this age group.
Therapeutic Class:
Antiparkinsonian Medications
Storage Instructions:
Store in a cool, dry place away from light. Keep out of reach of children.










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.