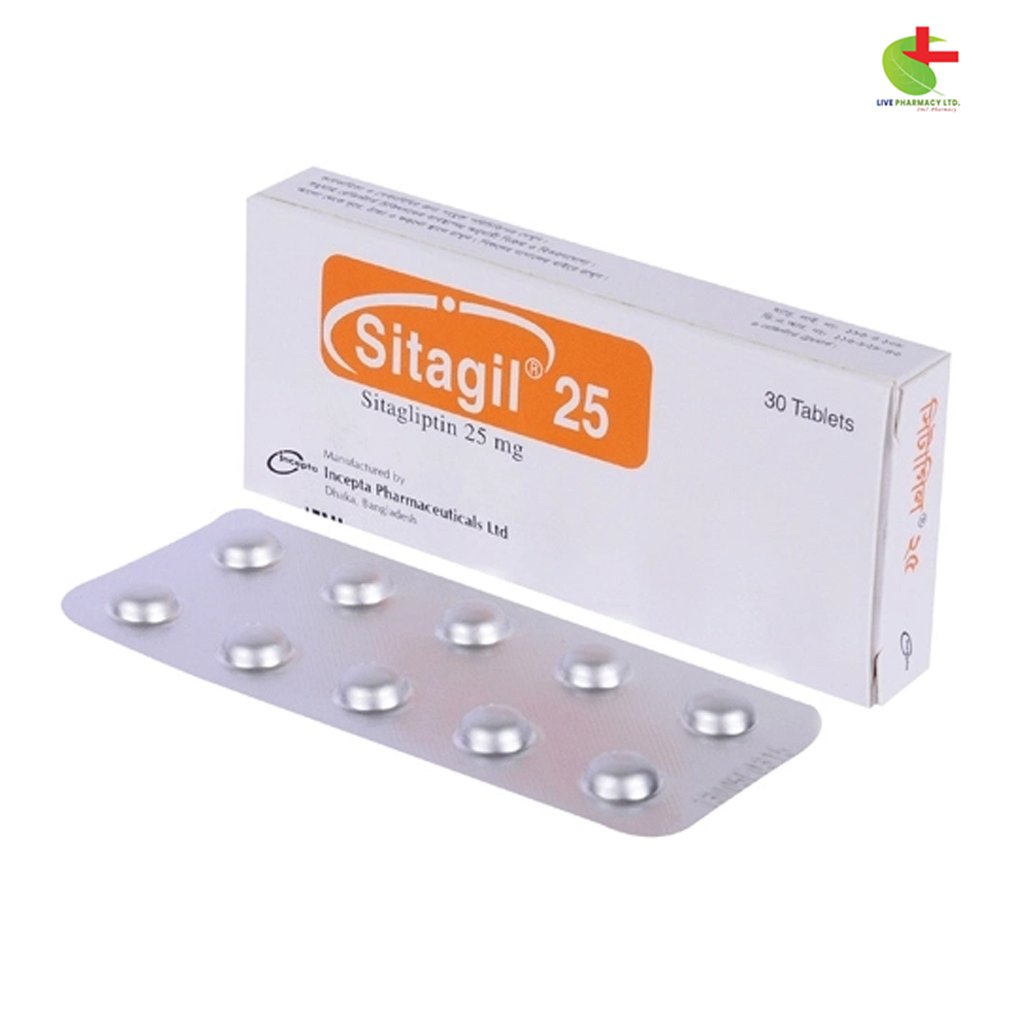
Sitagil 25
80.00৳ Strip
- Sitagil is a DPP-4 inhibitor used to improve blood sugar control in adults with type 2 diabetes.
- It works by increasing incretin hormone levels, which enhance insulin release and reduce glucose production.
- Sitagil is taken once or twice daily, with or without food.
- It can be used in combination with other diabetes medications.
- Always follow the guidance of a registered healthcare provider for proper use.
 Brand
Brand
|
Incepta Pharmaceuticals Ltd |
|---|---|
 Generics
Generics
|
Sitagliptin |
 Type
Type
|
Tablet |
Indications
Monotherapy & Combination Therapy: Sitagil is used as an adjunct to diet and exercise for improving blood sugar control in adults with type 2 diabetes. It helps manage glycemic levels in diabetic patients, promoting better overall control of the condition.
Limitations: Sitagil is not suitable for type 1 diabetes or the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis. The drug has not been studied in patients with a history of pancreatitis, and its safety in these individuals remains unknown.
Consult a registered physician for proper use of Sitagil.
Pharmacology
Sitagliptin is a DPP-4 inhibitor that enhances the action of incretin hormones in the body, such as GLP-1 and GIP. These hormones are responsible for regulating blood sugar by promoting insulin secretion and reducing glucagon release. Sitagliptin helps extend the life of these incretin hormones, supporting better insulin production and glucose balance.
Dosage & Administration
- The recommended dosage for Sitagil is 50 mg twice daily or 100 mg once daily.
- Sitagil can be taken with or without food.
Follow the dosage guidelines as prescribed by a healthcare professional.
Drug Interactions
Sitagil does not significantly alter the pharmacokinetics of drugs like metformin, glyburide, simvastatin, or warfarin. However, it may slightly increase digoxin levels without the need for dose adjustment.
Contraindications
Sitagil should not be used by individuals with a history of serious hypersensitivity reactions such as anaphylaxis or angioedema.
Side Effects
Common side effects include:
- Headache
- Upper respiratory tract infection
- Nasopharyngitis
- Hypoglycemia may occur, especially when used in combination with sulfonylurea or insulin.
Pregnancy & Lactation
- Sitagil is classified under Pregnancy Category B. While animal studies show no significant risks, it should be used during pregnancy only if necessary.
- Lactation: Sitagliptin is secreted in rat milk, but it is unknown if it is excreted in human milk. Caution is advised for nursing women.
Precautions & Warnings
- Pancreatitis: If signs of pancreatitis occur, Sitagil should be discontinued immediately.
- Renal Insufficiency: Dosage adjustment is necessary in patients with moderate to severe renal impairment or those requiring dialysis.
- Hypoglycemia: Close monitoring is required when Sitagil is combined with other medications like insulin or sulfonylurea.
- Serious Hypersensitivity Reactions: Discontinue Sitagil if any hypersensitivity symptoms (e.g., Stevens-Johnson syndrome) arise.
Use in Special Populations
- Pediatric Use: The safety and efficacy of Sitagil in children under 18 have not been established.
- Geriatric Use: Elderly patients may require dosage adjustments due to age-related renal function decline.
Overdose Effects
In clinical trials, Sitagil doses up to 800 mg were well tolerated, with only slight increases in QTc intervals observed. In case of overdose, supportive care is recommended, and hemodialysis may help remove the drug from the body.
Therapeutic Class
- Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 (DPP-4) Inhibitor
Storage Conditions
Store Sitagil below 25°C in a dry place, away from direct light. Keep out of reach of children and do not use after the expiration date.










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.